(Blood Pressure Test, Blood Pressure Measurement, BP Test, BP Measurement)
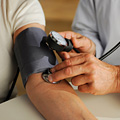
A patient having her blood pressure taken.
A blood pressure test monitors your blood pressure, a measure of the force of blood inside your arteries. Blood pressure should be measured regularly as a part of routine physical exam to screen for high blood pressure (hypertension), which can lead to a number of complications such as stroke and heart disease.
A blood pressure test should be done at least once every 2 years. If you have additional risk factors such as family history of high blood pressure and heart disease, you should monitor your blood pressure more often. In addition, blood pressure tests may be used to monitor the effectiveness of certain medications or lifestyle changes in lowering blood pressure.
Risks and precautionsThere are no risks or complications related to the blood pressure test. You may however experience some discomfort from the blood pressure cuff.
During the testThe test is often performed in doctor's offices or clinics by a nurse or a doctor, and it usually takes about 1 minute. During the test, do not talk or move.
- Start by placing your arm slightly bent on a table so that your arm is at the same level as your heart.
- Your doctor or nurse will wrap an inflatable cuff around the top of your arm and place a stethoscope just above the elbow over an artery in your arm. A circular dial attached to the cuff displays pressure.
- The cuff is then inflated to momentarily stop the blood flow in that artery. Your doctor or nurse will then slowly release the air in the cuff while listening to the pulse of your arm artery in the stethoscope.
- The systolic pressure, the peak pressure that occurs when the heart contracts, is recorded as your doctor or nurse hears a pulsing or tapping sound through the stethoscope.
- The diastolic pressure, the blood pressure when the heart is relaxed, is recorded when the pulsing sound disappears.
It is also possible to measure your blood pressure through an automated machine.
Before the testYou should wear a short-sleeved shirt to your blood pressure test. Go to the washroom to empty your bladder before the test and avoid drinking caffeinated beverages, eating, and smoking for about one hour before the test. You should not exercise for about half an hour before the test. Rest for at least 5 minutes before you start the test. Sit comfortably and make sure that both your feet are on the floor.
If you are taking any prescription or over-the-counter (non-prescription) medications, supplements, or herbal products, make sure you inform your doctor or pharmacist. Ask them whether it is necessary for you to stop taking any of these medications and products before the test. It is also important to tell them if you have allergies to certain medications, bandages, latex, or have other medical conditions.
After the testYour health care provider can tell you what your blood pressure is right after the test, and you can resume your normal daily activities. Your doctor can then discuss with you what the result means. A healthy blood pressure is 120/80 millimetres of mercury (mm Hg), also called "120 over 80." You may need additional tests if your doctor finds that you have high or low blood pressure.
If your doctor finds that you have hypertension (high blood pressure) or prehypertension (borderline high blood pressure), you should discuss with your doctor strategies to lower your blood pressure. Examples of such strategies may be lowering salt intake and quitting smoking and alcohol.
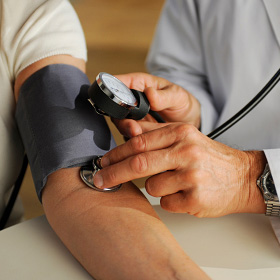
A patient having her blood pressure taken.