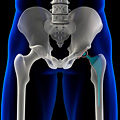
A 3D illustration of an artificial hip.
Hip replacement surgery is performed to reduce pain and improve activity levels caused by a diseased hip joint. It involves replacing a damaged hip joint with an artificial one called a prosthesis to improve joint functioning. The surgery is commonly done when there is hip joint damage caused by conditions such as:
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- hip injury or fracture
- bone tumours
Hip replacement surgery is performed by an orthopedic surgeon in a hospital.
Risks and precautionsIn general, surgery and the use of anesthesia comes with some risks that are associated with factors like your health and what the surgery involves. Side effects are very rare but can include trouble breathing, reactions to the anesthetic, bleeding, infection, scarring, and death.
Hip replacement surgery is usually a straightforward and safe procedure. However, there are some risks of complications or side effects, including:
- blood clots
- changes in the length of your leg
- dislocation, loosening, or stiffening of the new joint
- fractures
Get immediate medical assistance if you experience any of these complications or side effects.
It is important that you understand all the risks of complications and side effects of the procedure, and what you or your doctor can do to avoid them. Make sure that your doctor is aware of all your concerns.
Some people may experience complications or side effects other than those listed. Check with your doctor if you notice any symptom that worries you after your procedure.
During the test
- You will be given an anesthetic that will either numb your body below the waist or make you fully unconscious.
- The orthopedic surgeon will make an incision on the outside of your hip and remove the damaged bone and tissue.
- Once they are removed, the new prosthesis joint is inserted, and the surgeon will test it to make sure it moves well and is stable.
- The incision is then closed and you will be moved to the recovery room.
The procedure usually takes 1 to 3 hours.
Before the testIt is important that you fully understand what the procedure involves beforehand. Ask your doctor to explain the risks, benefits, and drawbacks of the procedure, and don't be shy to probe further until you are comfortable with your doctor's responses.
In preparing for hip replacement, you will meet with the orthopedic surgeon to discuss the surgery and any questions you might have. A preadmission check will be ordered, which may consist of several tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, electrocardiograms (ECGs), or blood tests.
You may not be able to eat or drink before the procedure; it is important to follow the timing that your doctor recommends, otherwise you run the risk of the surgery being cancelled or postponed. In general, people are advised to not eat for 8 hours before the procedure and most hospitals ask that you do not drink or eat anything after midnight the night before the procedure.
If you are taking any prescription or over-the-counter (non-prescription) medications, supplements, or herbal products, make sure you inform your doctor or pharmacist. Ask them whether it is necessary for you to stop taking any of these medications and products before the procedure. It is also important to tell them if you have allergies to certain medications, bandages, latex, or have other medical conditions.
Plan to have someone drive you home from the hospital. You should find out whether you will need to purchase any special equipment before you have the surgery so that you are prepared when you get home.
You will also need someone to assist you with daily activities for at least a week after you leave the hospital.
After the testYou will need to lie in bed for several days after surgery. It is normal to feel these side effects after this procedure:
- pain or discomfort
- limited movement
- swelling in the legs
If you were given general anesthesia before the surgery, you will be assigned to a hospital recovery room immediately after the surgery. As the anesthesia wears off, you may feel sore, groggy, or nauseous. Nurses will be available to assist you.
After the anesthetic wears off, you will be required to stay in the hospital overnight, at which point you will be moved to a regular ward for the rest of your stay. Most people usually remain in the hospital for about 3 to 5 days. Before you are released, the doctor or nurse will explain the steps you need to take to complete your recovery at home. You will be seen by a physical or occupational therapist who will show you exercises to help healing and ways to move to keep you safe.
Your surgeon will follow-up with you after the surgery to ensure that you are recovering well from the surgery. In general, many people are able to slowly resume some their activities after 6 to 8 weeks, but it can take up to 6 months to fully heal. Ask your doctor about the steps you can take (i.e., physical therapy) to speed up the recovery process.
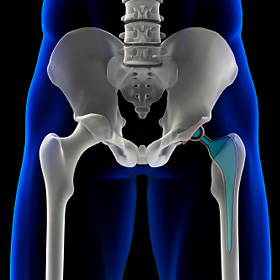
A 3D illustration of an artificial hip.